Adv. Mater., 2019, 1901666.
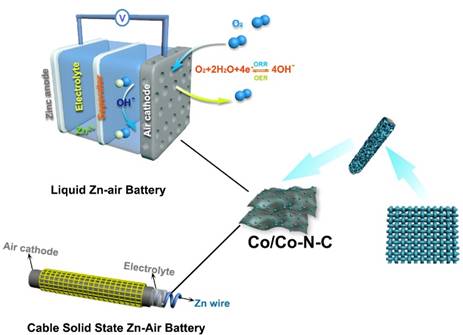
Peng Yu, Lei Wang*, Fanfei Sun, Ying Xie, Xu Liu, Jingyuan Ma, Xiuwen Wang, Chungui Tian, Jinghong Li*, Honggang Fu*. Co nanoislands rooted on Co-N-C nanosheets as efficient oxygen electrocatalyst for Zn-air battery. (Adv. Mater., 2019, 1901666.)
Developing non-precious-metal bifunctional oxygen reduction and evolution reaction (ORR/OER) catalysts is a major task for promoting the reaction efficiency of Zn–air batteries. Co-based catalysts have been regarded as promising ORR and OER catalysts owing to the multivalence characteristic of cobalt element. Herein, the synthesis of Co nanoislands rooted on Co–N–C nanosheets supported by carbon felts (Co/Co–N–C) is reported. Co nanosheets rooted on the carbon felt derived from electrodeposition are applied as the self-template and cobalt source. The synergistic effect of metal Co islands with OER activity and Co–N–C nanosheets with superior ORR performance leads to good bifuctional catalytic performances. Wavelet transform extended X-ray absorption fine spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy certify the formation of Co (mainly Co0) and the Co–N–C (mainly Co2+ and Co3+) structure. As the air-cathode, the assembled aqueous Zn–air battery exhibits a small charge–discharge voltage gap (0.82 V@10 mA cm−2) and high power density of 132 mW cm−2, outperforming the commercial Pt/C catalyst. Additionally, the cable flexible rechargeable Zn–air battery exhibits excellent bendable and durability. Density functional theory calculation is combined with operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy to further elucidate the active sites of oxygen reactions at the Co/Co–N–C cathode in Zn–air battery.
